Minimizing data security threats and keeping operations safe is a demanding task that every enterprise grapples with daily. The proliferation of employees working from anywhere increases information security risks. In addition to the risks of work-from-home computers, your on-premises network devices, phone systems, and other infrastructure elements must be updated regularly and scanned for potential vulnerabilities. Understanding and implementing patch management best practices will set your company on track for a strong security foundation.

Vulnerability management and patch management are two fundamental information security practices. Vulnerability management helps you identify potential cybersecurity risks while patching is good infrastructure hygiene. When functioning correctly, they work together to help companies find and fix vulnerabilities and help properly allocate IT resources for maximum effectiveness.
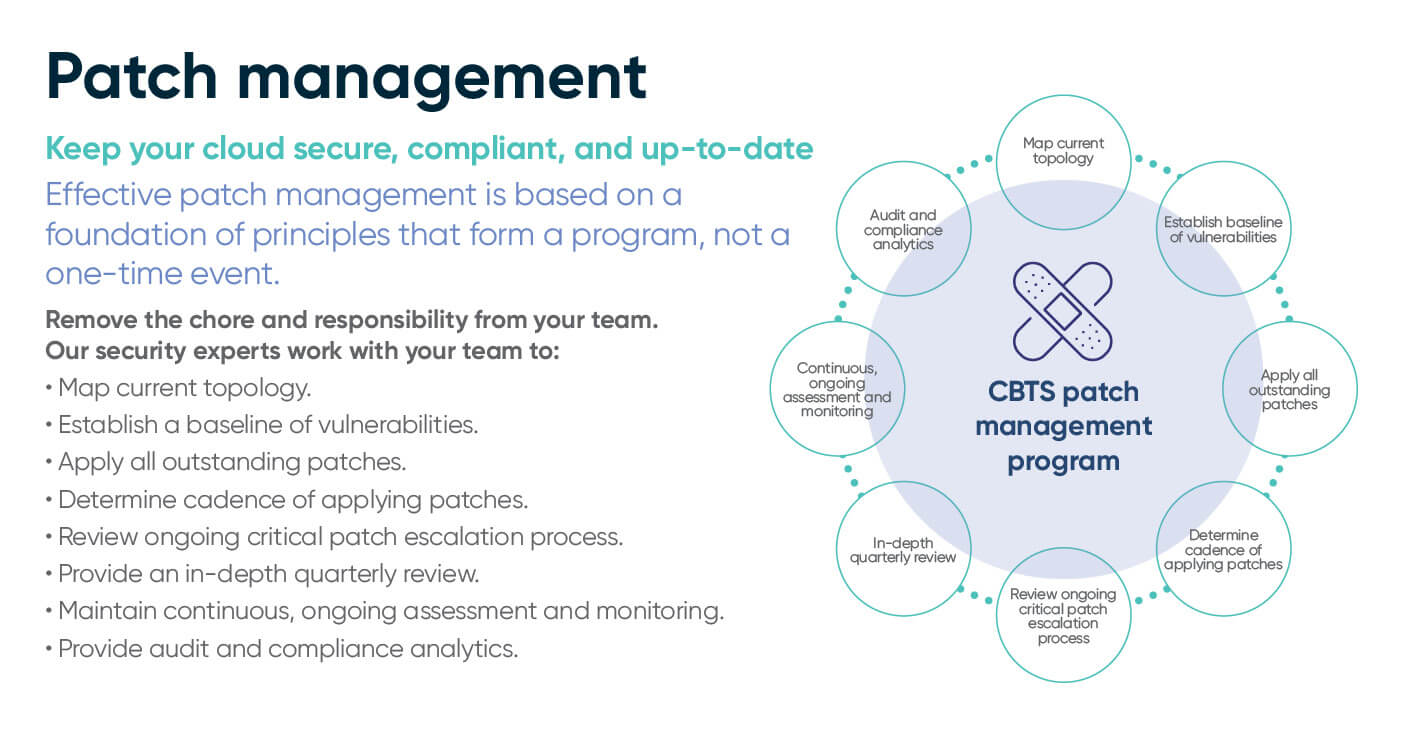
Successful vulnerability and patch management are not just one-time or occasional events. Instead, they must become full-fledged programs in your organization. Ideally, patching should be a monthly event, monitoring vulnerabilities as they are discovered. To cover all the angles of your operations, a thorough and ongoing process of assessment, preparation, deployment, and support is needed.
Best practices for a comprehensive patch management program include the following:
Learn more: Zero day vulnerabilities and their patches: I just met a vuln named Follina
With the above components in mind, enterprises concerned about the effectiveness of their patch management strategies should be sure to carefully exercise best practices. Alternatively, organizations overwhelmed by these steps could seek an experienced patch management provider like CBTS to set up and maintain the program. CBTS can also provide guidance and support for each phase of the process.
An audit of an enterprise’s software environment, hardware, and assets provides a better understanding of risk, vulnerabilities, and aids in prioritizing patches. This inventory provides a topography of current systems and what areas need the most attention. Whenever new applications or infrastructure is added to your organization’s technology stack, your “patch map” must be updated to reflect the additions to the patching program. Special care should be taken to assess third-party application vendors and what vulnerabilities they are adding to your environment.
After your organization has an up-to-date picture of its entire software and hardware landscape, it can effectively assign relative risk levels to each program or system. The higher the risk level, the faster it should be addressed in your patch management strategy. Additionally, if multiple versions of redundant software have accumulated in your portfolio, these can be consolidated to mitigate the risk of exposure from outdated applications.
A managed service provider can aid in analyzing and prioritizing your inventory and deploy automation tools that reduce manual legwork.
Other factors that determine patch prioritization include:
Learn more: Top five cybersecurity actions to take right now
If your organization utilizes a third-party vendor for some of its software solutions, involving this vendor in your patch management approach is crucial. Third-party software should be kept up-to-date alongside your proprietary software to ensure that your network environment is up-to-date. Third-party applications need to be updated, just like your other systems and hardware, to plug vulnerabilities that arise.
Other factors to consider when setting up the policies of your patch management program include:
There are risks when applying new patches to a system, even when you do thorough testing. That’s why creating full system backups for the affected assets is vital before patching. This ensures that your team has a working version to revert to if there is a problem with the patch.
Test and document deployed patches in non-production environments
A vital best practice of patch management involves testing patches in a non-production environment for critical systems. This sandbox or test environment should match your actual system as much as possible—the same hardware, applications, and other assets—to ensure that any issues can be traced and fixed before rolling out to production.
Caution is almost always preferable to speed when it comes to security. To that end, when implementing the tested patch, utilize a phased rollout where you patch your critical production servers after they clear the testing phase, then move to less critical systems.
Experienced patch management as a service providers work on a 30-day timeline to ensure systems stay up-to-date. When possible, patching takes place after hours to avoid potential service disruptions. The major exception to this schedule is urgent security patches known as “out-of-band” releases. These patches are released as needed and sometimes must be implemented on an accelerated timeline.
Patch Tuesday is the term Microsoft uses for the second Tuesday of each month when they releases major patches. Other vendors have adopted this kind of monthly cycle as well, though not all do so on the second Tuesday.
Watch this episode of Inside the CISO’s Office where CISO John Bruggeman and Jon Lloyd discuss the unnecessary risk organizations take by missing patches, and how to patch smarter, not harder.
Establishing and systemizing the best practices for vulnerability and patch management is time-consuming. Choosing patch and vulnerability management services from CBTS gives your business more time and these additional benefits:
A managed vulnerability assessment and patch management program by CBTS covers every aspect of your network environment, from your endpoints to critical assets, equipment, and facilities. It also extends from the planning and deployment phases to an ongoing monitoring and auditing period, ensuring that your organization’s patch schedule is optimized for your specific needs. The security team at CBTS is home to some of the most knowledgeable cybersecurity experts in the industry. Their knowledge of cutting-edge tools and processes is ideally suited to guide your organization toward a robust cyber defense.
Contact CBTS for more information on vulnerability assessment and patch management services.